Looking back at the 19th and 20th century, innovations and cutting edge technologies have been developed in neither space nor computer sciences, but in the field of genetics, cell based medicine and nanotechnology. These novel diagnostic and therapeutic technologies are the need of the hour as the world is seeing an alarmingly rapid rise in occurrence of diseases. Cell based therapy is one such gift to mankind which is showing immense potential in management of conditions that were previously thought to be untreatable. This form of therapy addresses the root cause of problems rather than palliative management of symptoms.
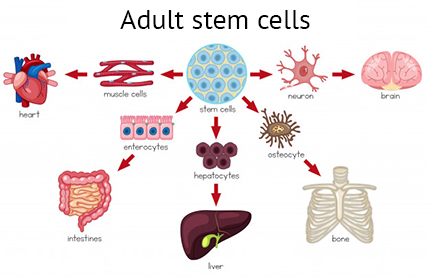
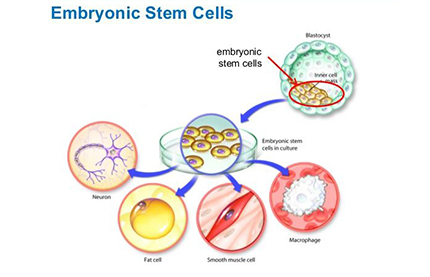
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells and are of two types, namely, embryonic (from the embryo) and adult stem cells. Although embryonic stem cells are more potent, the ethical and legal considerations have raised concerns regarding their use. Adult stem cells that were earlier assumed to be present only in the bone marrow have now been identified in different organs and tissue such as brain, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, ovarian epithelium etc. Furthermore, stemcells may be of hematopoietic (blood forming) or mesenchymal (organ/tissue associated) populations.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have the capacity for self renewal and differentiation into various tissues. MSCs are known to differentiate into tissues of mesodermal lineage such as bone, fat, muscle and cartilage. Additionally, they also possess the property of trans- differentiation, which is the ability of one type of cell to differentiate into another cell type based on the environment. The role of adult stem cells in the human body is to participate in organ homeostasis, wound healing etc.
It is now known that MSCs can differentiate into tissues derived from a germ layer other than mesoderm. To this effect, neural differentiation of MSCs has been reported which holds promise to develop treatment strategies for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s disease etc.
Mesenchymal stem cells act as medicinal signaling agents and unlike drugs, are not single molecular agents. These cells are adaptive agents capable of complex functions involving many bioactive factors. These multi-potent cells may be called medicinal drug stores of the body. Homing to the site of injury occurs primarily as a result of local production of inflammatory mediators during tissue damage. The cells then secrete considerable levels of immunomodulatory and trophic factors which aid in cell replacement, enhancement of organ function etc. by harnessing their innate regenerative potential. MSCs exert a paracrine effect during active tissue inflammation, therefore therapy is most effective during early stages of a disease. By this mechanism, MSCs enhance migration of cells associated with wound healing into damaged tissues/organs and induce their proliferation, thereby accelerating the healing process.
Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) therapy for various blood related malignancies have been carried out successfully for more than 5 decades. However, HSCs are prone to differentiation and therefore it is difficult to maintain in their stem cell potential. MSCs on the other hand can be induced to proliferate while maintaining their undifferentiated multi-potent stage. In addition, HSC therapy may be associated with an increased incidence of graft-versus-host-
disease (GVHD). Research is currently being done on immunomodulatory ability of MSCs which aims to: (i) Improve hematopoietic reconstitution after HSC therapy and (ii) Overcome GVHD upon allogeneic transplantation.
For the above mentioned reasons, from a therapeutic perspective, mesenchymal cellular therapy is also emerging as an extremely promising approach for tissue regeneration owing to the availability, ease of harvest and transplant of cells (no surgical procedure involved). Orthopedic conditions such as avascular necrosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid
arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy, stroke etc., as well as diabetes, liver, genitourinary disorders, dermatological conditions and many more can achieve benefits from cellular therapy.
An interesting avenue of research on MSCs is pertaining to cancer immune therapy wherein MSCs may behave as regulated delivery vehicles. The therapy is based on the principle of the immune system to detect transformed cells in the blood or from tumors and eradicate these via immunological processes. Mesenchymal stem cells associated with chemotherapeutic agents can function as target specific molecules that act against the cancerous cells.
Autologous cellular therapy is just the beginning of a new era in the world of regenerative medicine. Nonetheless, resources are being invested and breakthrough scientific efforts are being made in gaining fundamental knowledge about the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying MSC therapy.
Products may be developed using stem cells, however, accuracy, reliability, consistency and validity of the process should be ensured while considering development of such products. Current research also includes development of bioactive scaffolds that are capable of supporting activation and differentiation of host stem cells at the required site. In the future it will be possible to use human native sites as micro-niche/micro-environment for potentiate
of the human body’s site-specific response. The main goal of these advances is to harness the
potential of endogenous repair mechanisms/stem cells to promote tissue regeneration.




