Daniel Banda is a 49-year-old and is the owner of a hotel in Ibadan. He has 2 kids and a wife. He is a very happy and humble personality, and is always forthcoming to help others. He loves outings with his family.
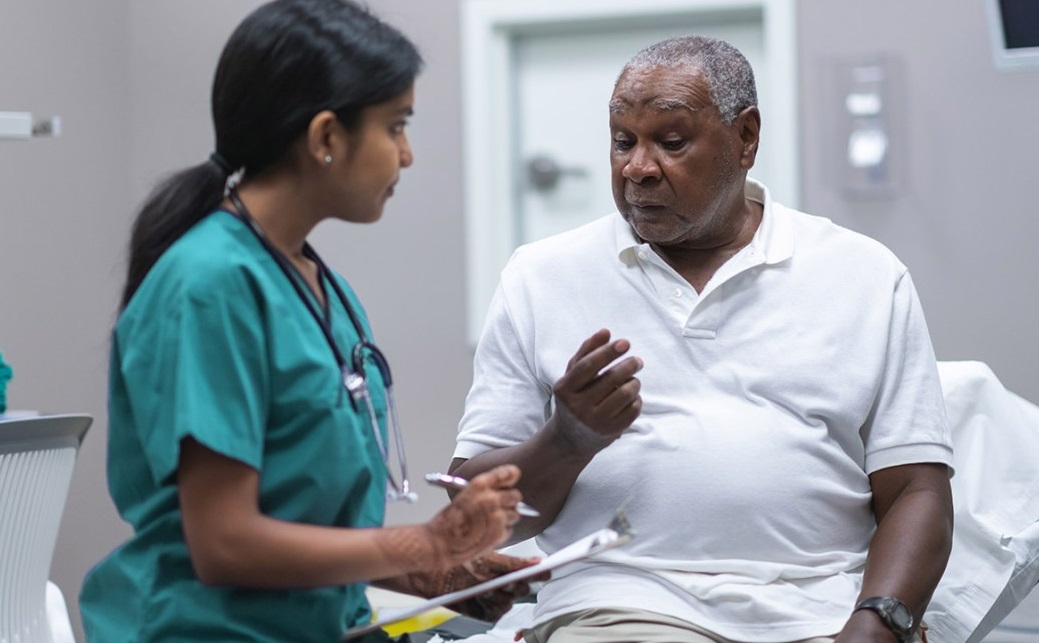
Two years back, Daniel started to notice burning sensations while urinating. Moreover, he also felt that his urine stream had also decreased.
He visited a local physician for a checkup. After a physical examination, the doctor suggested he do an ultrasound and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test.
The next day when the report came, the PSA levels were surprisingly high. The doctor got suspicious and recommended further evaluation including biopsy.
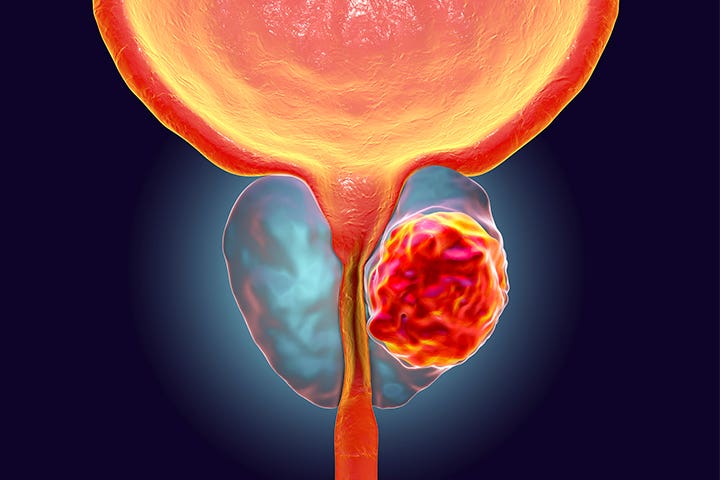
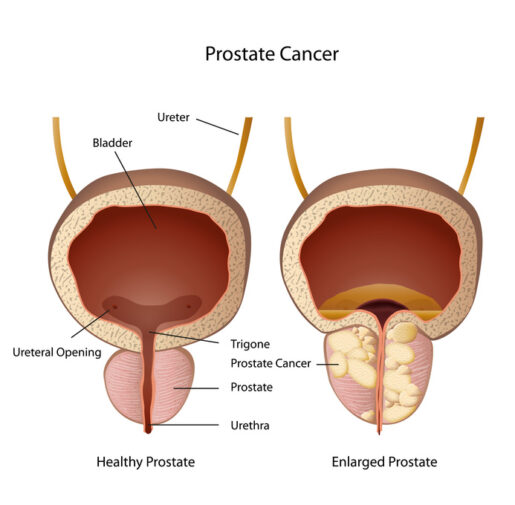
After the biopsy result, the doctor informed Daniel that he has localized prostate cancer.
After hearing the cancer news Daniel and his wife Abiola were in shock. His wife and kids supported him. The family wanted to undergo the best treatment for Daniel. His elder son started researching on the internet for the best treatment for prostate cancer.

While looking for options in India, he got to understand the Tumour board, a new way of deciding treatment plans by a team of doctors including medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, and Radio oncologists. He dropped an inquiry at the MedicoExperts website for a tumor board appointment.
The MedicoExperts patient care department got in touch with Daniel’s family and arranged the video consultation with the Uro-oncologist, who heads the board for prostate. The doctor went through all the reports and took a day more to discuss with team members.
A day later, the uro-oncologist shared the board view and the MedicoExperts patient care team passed the treatment plan with Daniel’s family.
The family requested once again to interact with the Onco-Urologist who was heading the board. One more video call got scheduled for the next day. The doctor explained the plan and the reasons behind the plan in detail. He also clarified the doubts which the family was having.
Though the treatment plan was a bit different than the conventional plans, the Daniels family decided to go with the board’s recommendations.
MedicoExperts patient care team helped the family with visas and other logistics arrangements.
After 15 days, Daniel and his wife came to India for treatment. Daniel was admitted on the same day and an evaluation was performed to check the current condition.
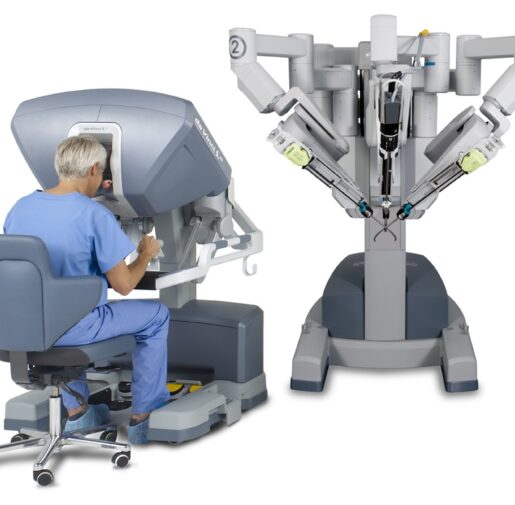
After the evaluation, the onco-surgeon performed the robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy to remove the impacted prostate along with cancerous tissues.
After a few days, the doctor conducted the evaluation and there is no trace of cancer found. The doctor advised Daniel for the follow-up appointments and to do PSA testing for 6 months. The doctor did mention that there might be a need for radiation in case of the PSA levels increase.
Daniel and his wife were very happy with the results and thanked the doctor and MedicoExperts.
Daniel went back to Ibadan and MedicoExperts helped Daniel to connect with the doctor for the follow-up through video consultation. Fortunately, Daniel responded to the treatment very well and as per the doctor’s expectations, he came out without any additional therapy.
This can be your story as well to win the battle against prostate cancer. What you need is the right guidance, right treatment at the right time from the experts.