The question on: is ovarian cancer treatable? The answer may surprise you.
Ovarian cancer is a topic that often raises many questions, concerns, and fears. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of the condition to make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Is ovarian cancer treatable?
The answer is not only resounding clear but also a promise of healing, strength, and a brighter tomorrow.
Join us as we take a look into the facts of ovarian cancer’s treatability, a guide on the importance of early detection, symptoms, causes, stages and the belief that your health matters above all else.
According to the National Cancer Institute, around 6.3 per 100,000 people die from ovarian cancer each year.
But even before we get into this question let’s understand some important aspects associated with Ovarian Cancer.
How Serious is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. It’s one of the most destructive gynecological cancers, but its prognosis greatly depends on the stage at which it’s diagnosed.
In its early stages, ovarian cancer is more treatable, while advanced stages may present significant challenges.
Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a substantial difference in outcomes.
What is the Importance of Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer?
Early detection plays a pivotal role in the treatability of ovarian cancer.
When the disease is caught in its early stages, the chances of successful treatment and even a cure are significantly higher.
But the approach may vary depending on various factors, including:
- the stage at which it’s diagnosed and
- the specific characteristics of the cancer cells.
Regular check-ups and awareness of the common signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer can be life-saving.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
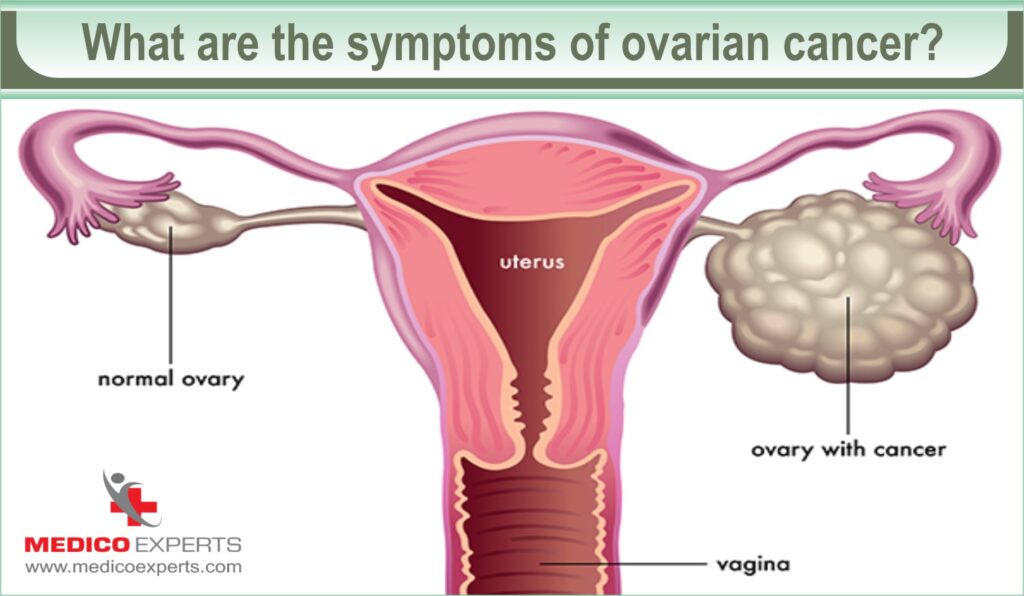
Ovarian cancer is often called the “silent killer” because it can develop without showing obvious symptoms in its early stages.
However, as the disease progresses, some women may experience symptoms.
It’s essential to be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention if you notice them, especially if they are persistent and unusual for you.
Here are the common symptoms of ovarian cancer:
Abdominal or Pelvic Pain:
Persistent pain in the abdomen or pelvis, especially if it is new and unrelated to your menstrual cycle or other known causes, should be evaluated.
Bloating:
Unexplained and persistent bloating that doesn’t improve with changes in diet or medication.
Feeling Full Quickly:
If you feel full quickly when eating and have a reduced appetite, it could be a symptom of ovarian cancer.
Frequent Urination:
An increased need to urinate or changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
Changes in the Menstrual Cycle:
Any changes in your menstrual cycle, such as irregular periods or postmenopausal bleeding.
Back Pain:
Lower back pain can be a symptom of ovarian cancer in some women.
Fatigue:
Persistent, unexplained fatigue or low energy levels.
Indigestion:
Chronic indigestion or heartburn that doesn’t improve with antacids.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by various other conditions, and having these symptoms does not necessarily mean you have ovarian cancer.
However, if you experience any of these symptoms, and they are unusual for you or persist for more than a few weeks, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
What are the causes of ovarian cancer?
The exact causes of ovarian cancer are not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to the development of this disease. Ovarian cancer is a complex condition, and multiple factors can increase the risk of its occurrence.
Here are some potential causes and risk factors associated with ovarian cancer:
- Age
- Personal History
- Family History
- Inherited Gene Mutations
- Endometriosis (a condition in which tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, may have an elevated risk)
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) (long-term use of estrogen-alone hormone replacement therapy, without progesterone, can increase the risk of ovarian cancer)
- Infertility and Fertility Drugs
- Obesity
It’s important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean you will develop ovarian cancer. Many women with one or more risk factors never develop the disease, and some women without known risk factors can develop ovarian cancer.
Is Ovarian Cancer Genetic?
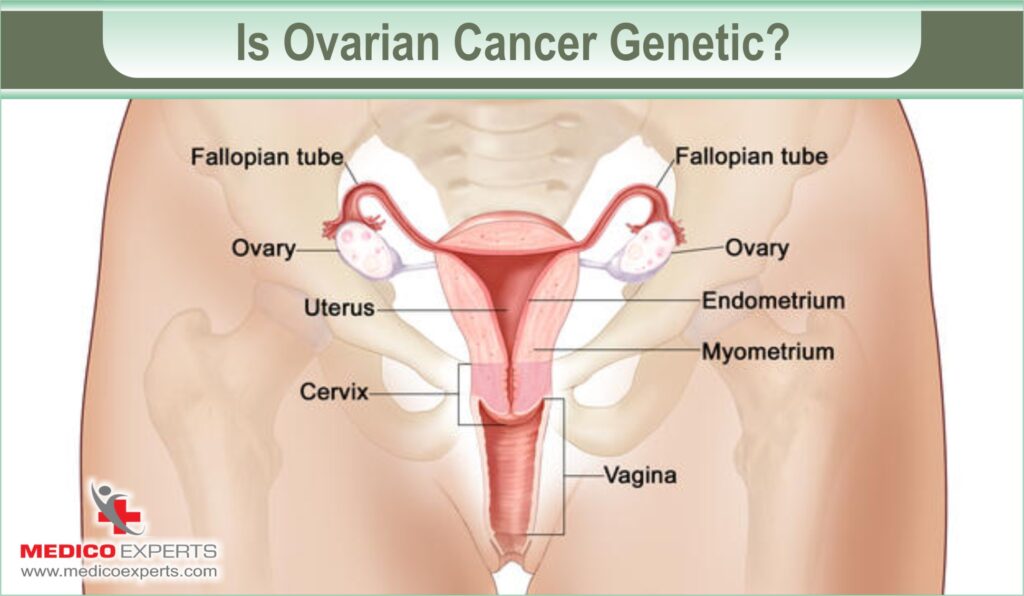
Ovarian cancer can sometimes be linked to genetics. If there is a history of ovarian cancer in your family, your chances of developing the disease may be higher.
However, it’s crucial to remember that not all cases of ovarian cancer are genetic. Most cases occur in women with no family history of the disease.
Let us now take a look at the stages of ovarian cancer.
What Are The Stages of Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is typically classified into stages to determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment decisions.
Following are the stages of ovarian cancer:
Stage I:
1. The cancer is present in either one or both of the ovaries.
2. It may involve the surface of the ovaries.
3. The lymph nodes and other organs remain unaffected.
4. Stage I is further divided into sub-stages (IA, IB, IC) based on the extent of the cancer within the ovaries and pelvis.
Stage II:
1. Cancer has spread beyond the ovaries, but it is still within the pelvic region.
2. It may involve the uterus, fallopian tubes, or nearby tissues.
3. Other organs and lymph nodes are not affected.
4. Like Stage I, Stage II is also divided into sub-stages (IIA, IIB, IIC) based on the extent of the spread within the pelvis.
Stage III:
1. Cancer has extended beyond the pelvis into the abdominal cavity.
2. It may involve the omentum (a fatty tissue layer), the lining of the abdomen, or other abdominal organs.
3. Lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen may be affected.
4. Stage III is divided into sub-stages (IIIA, IIIB, IIIC) based on the size of tumor deposits and lymph node involvement.
Stage IV:
1. This is the most advanced stage.
2. Cancer has spread to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or other organs outside the abdominal or pelvic regions.
3. This stage may also include pleural effusions (fluid around the lungs) with cancer cells.
4. Stage IV indicates the cancer’s widespread presence in the body.
Early-stage ovarian cancer (Stage I and II) is more likely to be curable with treatment, while late-stage disease (Stage III and IV) presents greater challenges.
Accurate staging is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan for each patient.
Get comprehensive information on advanced treatment options here.
Let us move ahead with some tips and guidance related to ovarian cancer.
Practical Tips and Guidance Related to Ovarian Cancer to Navigate this Challenging Journey with Confidence.
Each individual’s journey with ovarian cancer is unique, and the tips provided here are general guidance. Always consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific situation and stage of ovarian cancer.
Early Detection Saves Lives:
- Detection at an early stage is crucial.
- Successful treatment and even a cure are much more likely when ovarian cancer is detected early.
Genetic Counseling and Testing:
- For those with a family history of ovarian cancer or certain genetic mutations, seeking genetic counseling and testing is an essential step.
- It can help you understand your risk and make informed decisions about preventive measures and regular screenings.
Personalized Treatment:
- The treatment of ovarian cancer is not one-size-fits-all.
- Your healthcare team will work with you to create a personalized treatment plan based on the type and stage of your cancer, your overall health, and your individual preferences.
Support and Resources:
- Coping with ovarian cancer is a journey that requires a strong support system.
- Your emotional and mental well-being is as crucial as your physical health.
Clinical Trials:
- Consider participating in clinical trials if the opportunity arises.
- These trials pave the way for new, innovative treatments that may change the landscape of ovarian cancer care in the future.
Palliative Care:
- For those in advanced stages of the disease, palliative care can provide relief from symptoms, pain management, and emotional support.
- Your comfort and quality of life remain a priority.
Your health matters, and you have the power to make informed choices throughout your treatment and recovery.
Conclusion:
We certainly believe that this information has provided you with a better understanding of ovarian cancer and its treatability.
The short answer is yes, ovarian cancer is treatable, but the success of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed, the type of ovarian cancer, the individual patient’s health, and various other aspects mentioned above.
Your health is one of the most valuable assets you possess, and when facing a diagnosis of ovarian cancer, significance is magnified.
Ovarian cancer is a challenging rival, but with timely awareness, the right approach, and access to appropriate medical care, the odds can be tilted in your favor.
Medicoexpert Tumor Board – Your Second Opinion Team
At Medicoexpert, we understand the importance of making well-informed decisions about your health. That’s why we offer a Tumor Board, a team of medical experts who can provide second opinions on your ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment plan.
We believe in empowering patients with the knowledge they need to make the right choices for their health.
We understand that each patient is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Our approach is comprehensive, focusing on both conventional and complementary therapies to provide the best possible care.
Book an appointment today!
FAQ :
Q1. Is Ovarian Cancer Contagious?
A. Ovarian cancer is not contagious. Physical contact cannot transmit it, unlike the common cold.
Q2. Is it Possible to Survive Ovarian Cancer?
A. Survival rates for ovarian cancer vary based on the stage at diagnosis and the specific characteristics of the cancer. Many women with ovarian cancer go on to live long and fulfilling lives after successful treatment.
Q3. How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
A. Ovarian cancer is diagnosed through a combination of methods, including a pelvic exam, blood tests, and imaging studies like ultrasounds and CT scans. However, the most definitive way to diagnose ovarian cancer is through a surgical procedure known as a biopsy.
Q4. Is ovarian cancer painful?
A. Ovarian cancer can be painful, but not all patients experience the same symptoms. Pain management is an essential part of treatment to ensure patients’ comfort. Your well-being is our priority, and Medicoexpert is here to support you every step of the way.
Q5. How treatable is ovarian cancer if caught early?
A. Ovarian cancer is highly treatable when caught early. The primary treatment is surgery to remove the tumor, with additional treatments like chemotherapy if needed.



