Early detection of cervical cancer increases the chances of successful treatment of pre-cancers and cancers.
To detect early, you need to know the early symptoms of cervical cancer.
More so, delays in detecting cancer can worsen the patient’s condition.
Shockingly enough cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers among women but in a majority of cases, the women fail to notice the early signs.
Treatment of Cervical cancer is most effective if the disease is detected at a very early stage. The treatments in the initial stages are very simple, Highly effective, and have success rates of more than 90%. Also, early detection of cancer prevents the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
By detecting it early you can lead a very normal pain-free life. You can lead a healthy marital life and fulfill all of your dreams as a very normal person.
Your ability to recognize the early signs of cervical cancer will prepare you to win the battle against cancer before the cancer starts impacting your body functions. Like Laila did,
Laila’s Story: A Real-Life Journey
Laila, from Dublin, had also suspected that she had cervical cancer. Laila believed in enjoying her life and meeting new people and making friends. While Laila was living a life of her choice she experienced some abnormal vaginal discharge.
Concerned Laila visited her gynaecologist who advised a PAP smear test for her. Once the PAP smear test report came Laila tested positive for HPV. Luckily Laila was cautious and noticed the early signs of cervical cancer and started the treatment.
The early initiation of treatment helped Laila to recover. Like Laila, you too can have better health outcomes for your cervical cancer if you initiate early treatment.
Let’s discuss the symptoms that can help you identify cervical cancer.
How did I know I had cervical cancer?
As said above, Liza got suspicious when she started to experience abnormal vaginal discharge and bleeding. As a result, she approached a doctor proactively, which in a way saved her life.
Some women with cervical cancer may experience symptoms, including:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding after sexual intercourse, bleeding between periods, or unusually heavy periods
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Unusual vaginal discharge, which may be watery, thick, or foul-smelling
- Pelvic pain or pain during urination
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, you should talk to your healthcare provider to determine the cause and whether further testing is needed.
Again, regular cervical cancer screening is the best way to detect cervical cancer early, before it has a chance to progress and cause symptoms. Regular cervical cancer screening, such as Pap tests, is very important for detecting cancer in its early stages when it’s most treatable.
Take charge of your cervical health and book a consultation with a cervical cancer specialist today. Don’t wait until it’s too late. Your health is important, and early detection is key. Schedule your appointment now and get the peace of mind you deserve.
What are the Early visible signs of Cervical Cancer?
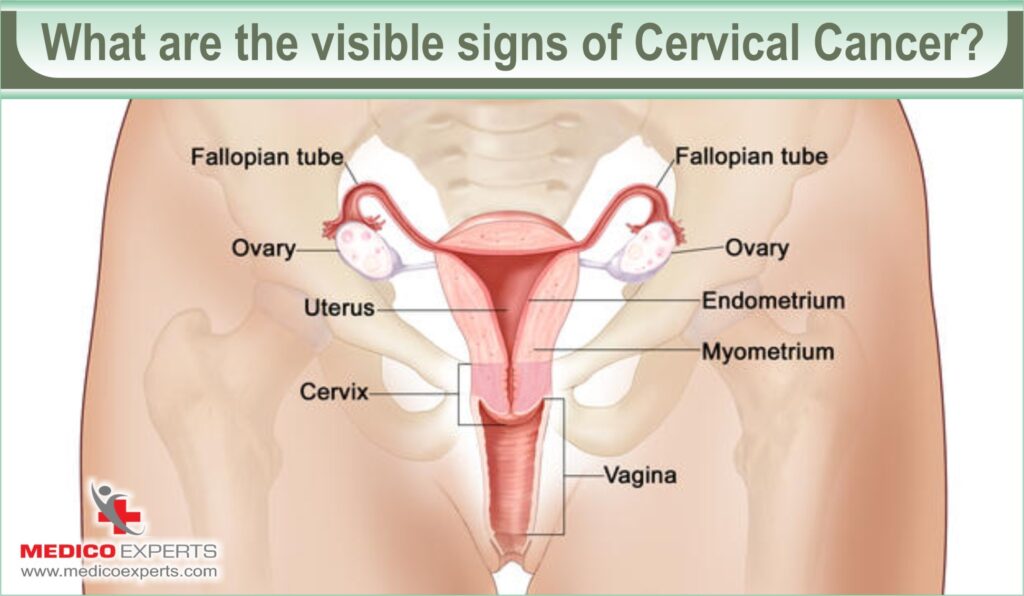
The typical earliest symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- Irregular blood spotting or light bleeding between periods in menstruating women
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse;
- Postmenopausal bleeding or spotting
- Bleeding after a pelvic examination
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge that has a bloody tinge to it.
However, with time as cervical cancer advances, more severe symptoms may appear like:
- Persistent pain in the lower back, leg, and pelvic area;
- Unexplained weight loss,
- Unexplained fatigue, and loss of appetite;
- Offensive vaginal discharge with vaginal discomfort because of profuse discharge.
- Swelling in the lower extremities.
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your doctor immediately. Regular screenings like Pap smears can detect cervical abnormalities before they progress.
What are the causes of cervical cancer?
Studies suggest HPV or Human Papillomavirus is the main cause of cervical cancers. Certain strains of the HPV can change in the cervical cells which may sometimes cause abnormal cell growth resulting in cancer.
Apart from HPV, taking certain medications to prevent miscarriage during pregnancy puts the female fetus at risk of developing cervical cancer.
Apart from these two known factors that may cause cervical cancer scientists are researching to know more about the cause of cervical cancer.
What Is HPV and How Does It Cause Cervical Cancer?
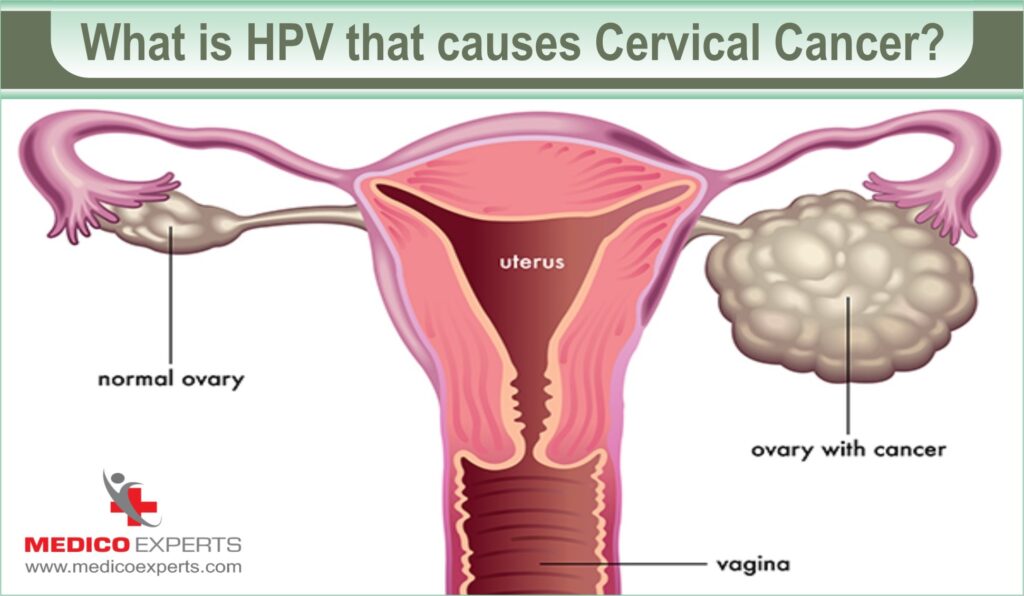
HPV or Human Papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted virus that often causes cervical cancer. The virus often causes genital warts. Besides, causing cervical cancer some strains of HPV can cause:
- Anal cancer
- Vaginal cancer
- Vulvar cancer
- Throat cancer
However, not all HPV virus strains cause cervical cancer. There are only a few strains that cause cervical cancer.
Sometimes there might not be any early symptoms in women infected with HPV. So, it is always advisable for sexually active women to undergo a PAP smear test once every year.
How serious is your cervical cancer?
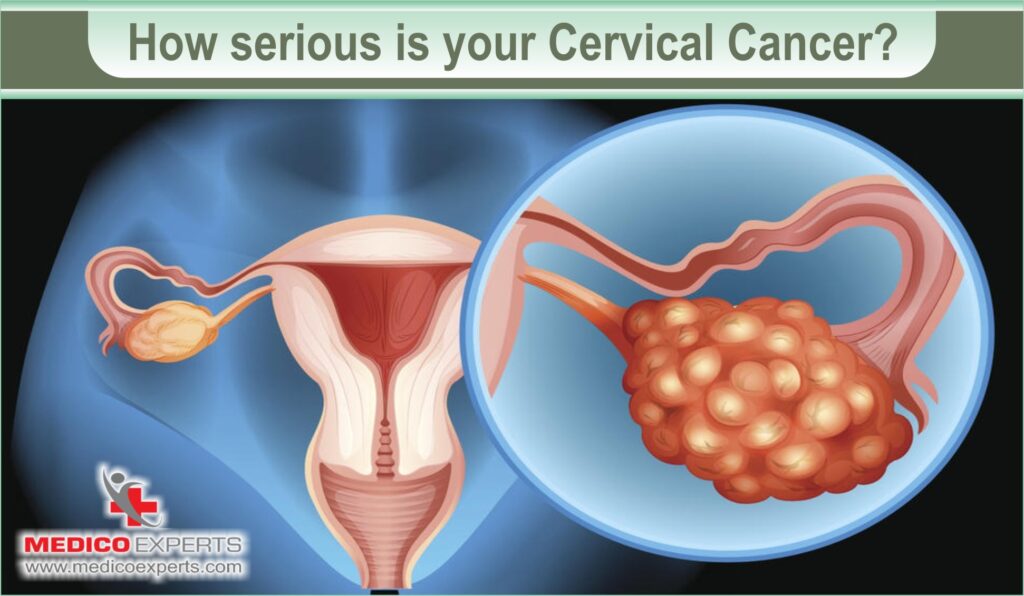
If your doctor has diagnosed cervical cancer for you they will try to find the extent of the spread of the cancer, this is called staging.
- Early Stages (Stages 1–2): Cancer is confined to the cervix and nearby tissues.
- Advanced Stages (Stages 3–4): Cancer has spread to distant organs.
Based on the stage, your doctor will recommend the most effective treatment plan.
How can you prevent cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is common among sexually active young women and the ones who have multiple partners. Here are a few tips that young women can incorporate into their lives to prevent cervical cancer:
- Get vaccinated against HPV: The HPV vaccine can prevent most cases of cervical cancer. It’s most effective when given before exposure to the virus, ideally in adolescence.
- Practice safe sex: Use condoms to reduce the risk of HPV transmission. Limiting the number of sexual partners also lowers your risk.
- Schedule Regular Screenings: Pap smears and HPV tests are essential for early detection. Women should begin screenings at age 21 and follow their doctor’s recommendations.
Tip: A combination of vaccination, safe practices, and screenings offers the best protection against cervical cancer.
Conclusion:
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common type of cancer among women and often goes unnoticed by women during the early stages.
However, by proper education about the early signs of cervical cancer women can understand the warning signs and initiate their treatment for cervical cancer at an early stage. By initiating treatment at an early stage women can ensure better health outcomes from the treatment.
Also, women must understand that having unsafe sexual intercourse with multiple partners can put them at risk of contracting HPV which may cause cervical cancer.
However, women can protect themselves from contracting HPV by practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated against HPV, and avoiding sexual encounters with multiple partners.
If you wish to know more about cervical cancer visit the cervical cancer page. Alternatively, if you wish to seek consultation for cervical cancer please feel free to contact us. If you are scared of confidentiality we ensure that your consultation with one of our empanelled doctors will be confidential.
Frequently asked questions
Q1. What are the different stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms or earliest symptoms of cervical cancer in females?
The different stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms include:
– Bleeding between the periods
– Putrid-smelling vaginal discharge
– Bleeding or spotting after menopause
– Loss of weight
– Loss of hunger
Q2. How do I get cervical cancer?
The known causes of cervical cancer are:
– Infection with HPV
– Consumption of certain drugs during pregnancy to avoid miscarriage
Q3. What is a PAP smear test for cervical cancer?
A PAP smear test for cervical cancer is the most common test used in screening for this type of cancer. During the PAP smear test, your doctor collects a few cells from your cervix. The collected cervical cells are then studied to detect any abnormalities that could result in cancer. PAP smear test helps detect cervical cancer at an early stage.
Q4. Can cervical cancer be fully cured?
Yes! Cervical cancer is curable. However, when detected at an early stage the health outcomes are better.
Q5. What are the risk factors for cervical cancer?
Women who have unprotected sex with multiple partners are at risk of developing cervical cancer. Apart from them, women who take certain drugs during their pregnancy to avoid miscarriage are risking their children developing cervical cancer.
Q6. What are the early signs of cervical cancer?
The early symptoms of cervical cancer are:
– Irregular blood spotting or light bleeding between periods in menstruating women
– Bleeding after sexual intercourse;
– Postmenopausal bleeding or spotting
– Bleeding after a pelvic examination
– Foul-smelling vaginal discharge that has a bloody tinge to it
References
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cervical-cancer/if-you-have-cervical-cancer.html
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer
- https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/pap-smear
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC145302/
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.



